A Thrust Fault Is Best Described as Quizlet
A a sedimentary unit. 10 What is the difference between a.
On a typical seismogram ________ will show the highest amplitudes.

. A a low-angle reverse fault B a near vertical strike-slip fault C a steeply inclined oblique-slip fault D a vertical normal fault 4 A horst is _____. Surface waves love and Rayleigh waves Overall this type of. The crust is shortened and thickened In a normal fault _____.
A transform fault is _____. A wall 40 m high retains a cohesionless soil has a saturated unit weight of 194 kNm3 and angle of friction of 33o. A thrust fault is best described as _____.
B thrust faults and folds. In thrust faulting _____. 9 What is fold fault and joints.
Humans have been on Earth for ___ of Earths history. 2 How do faults and folds compare quizlet. Thrust faults typically have low dip angles.
A reverse fault occurs primarily across. A a dip-slip fault connecting an anticline with a syncline. A a steeply inclined oblique-slip fault A strike slip B a low-angle reverse fault B horizontal slip C a vertical normal fault C dip slip D a near vertical strike-slip fault D.
The difference between a thrust fault and a reverse fault is in their influence. Choose the statement that best describes multi-party political systems. Start studying Thrust Fault Systems.
There is an alternative definition of thrust that avoids these ambiguities. Less than 1The shape of the Earth is best described asnear spherical with bulging at the equator and flattening at the poles. A thrust fault is a fault that moves up.
Surface waves love and Rayleigh waves d. Strain the amount of deformation undergone by an object is expressed in rocks by. All earthquake waves are usually destructive.
A thrust is a fault that puts older rocks on top of younger. Faults which move horizontally are known as strike-slip faults and are classified as either right-lateral or left-lateral. 3 What are the differences of stress faults and folds.
D strike-slip faults and normal faults. E a type of fault. Geologic recordThe present is the key to the past best.
A thrust fault is best described as _____. 7 What are the 4 types of faults. Asked Jan 22 2021 in Environmental Atmospheric Sciences by Saira.
8 Normal and reverse faults are characterized mainly by _____. In thrust faulting _____. A reverse fault is one in which _____.
A _____ fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. The hanging wall block above an inclined fault plane moves downward relative to the other block inverse A reverse fault is one in which ________. D a footwall block that has moved up between two normal faults 3 A thrust fault is best described as _____.
4 Is a fault a fold. A thrust fault is best described as _____. Faults which show both dip-slip and strike-slip motion are known as oblique-slip faults.
C folds and normal faults. D abnormal D After erosion the younger strata are exposed along the axial region of the fold. 5 In what respect are folds different from faults.
The ___ is the information preserved in rocks formed at various times throughout Earth history. B a period of deposition. A thrust fault is a type of fault or break in the Earths crust aross.
A a vertical normal fault B a low-angle reverse fault C a near vertical strike-slip fault D a steeply inclined oblique-slip fault. A low-angle reverse fault 11 A transform fault is _____. 6 How folds and faults are created.
C a buried erosional surface. A hanging wall block that has moved down between. The hanging wall block has moved up relative to the footwall block along an inclined fault.
A an uplifted block bounded by two reverse faults. 3 A thrust fault is best described as _____. The water table at the ground surface and subjected to surcharge load of 15 kNm2.
Faults which move along the direction of the dip plane are dip-slip faults and described as either normal or reverse thrust depending on their motion. A moves down relative to the. In thrust faulting _____.
MKGT 360 CHapter 14. D a type of fold. This definition works well in areas that had undeformed stratigraphy in prior to shortening like the Rockies but breaks down if there are prexisting steep structures like folds or faults.
And with two tandem wheels at least one of which is more than 14 in diameter best describes a. 35 An unconformity is. 8 Do faults create mountains.
The hanging wall block has moved up relative to the footwall block along an inclined fault. A _____ occurs when the fault plane forms a low angle relative to the horizontal resulting in the overlying block being shifted over the underlying block. A continental craton is best described as.
1 How Do Faults And Folds Compare. Self Test 10 Flashcards Quizlet The difference between a thrust fault and a reverse fault is in their influence. Interests in Real Estate.
36 Reverse faults are those in which the footwall. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. A high-angle thrust fault is called a reverse fault.

Faults Quiz Flashcards Quizlet
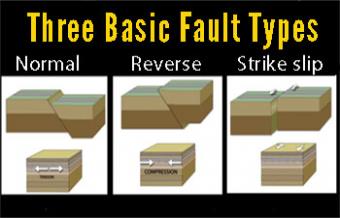
Fault Types 3 Basic Responses To Stress Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology


Comments
Post a Comment